polytrichum sporophyte
cells include: stereids, guide cells, hydroids and leptoids. It bears three rows of small brown or colourless leaves. Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. In vascular plants similar to green algae. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. The mid-rib forms the major part of the leaf. It is a dioecious plant, meaning that the male and female gametophytes are on separate plants. 3. By clicking Accept, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. The Gametophyte Generation. Fragmentation: The rhizome gives rise to erect lea& shoots at intervals. Czntral cell forms upper small venter canal cell and lover large egg cell. On the sideway from the radial strand, each group of leptoids is surrounded by a single layer of parenchymatous cells containing starch.
The nutrients in the solution surrounding the leaves are provided by dust particles blown in the wind, solutes dissolved in precipitation and solutes added to precipitation as it flows down the trees and shrubs in the forest canopy (if there is one), as well as solutes that may be carried up with capillary water from the substrate that the moss is growing on. Macro photo. Required fields are marked *. 2. 2. WebPolytrichum juniperinum. course there are always exceptions to these norms, but they are rare. The apophysis is the main photosynthetic region of the capsule. Polytrichum is dioeciuos, i.e., antheridia and archegonium are borne on different gametophores. It carries the capsule high into the air. green. The gametophore in Polytrichum is rhizomatous. The stereids are thick-walled supporting cells constituting the major part of the hydrom cylinder. Polytrichum is a genus of mosses commonly called haircap moss or hair moss which contains approximately 70 species that cover a cosmopolitan distribution. The basal portion of the sporophyte is the foot. Endothecium forms central conducting strands of apophysis. Plants live in cool and shady places. Internally, the erect stem is differentiated into the outermost superficial layer (epidermis), followed by the wide cortex, and the central cylinder. Transfer cells have convoluted cell walls External morphology is the external structure of Polytrichum.
 Any apical cell in the apical region acts an archegonial initial. Polytrichum is dioecious.
Any apical cell in the apical region acts an archegonial initial. Polytrichum is dioecious. Juniper haircap moss have very obvious male and female parts. Also, most mosses
The flask-shaped archegonia are borne at the apices of leafy stems. spirally arranged leaves that are one cell layer thick (unistratose). tissue that was once a part of the archegonium.
passed through transfer cells that lie in the placental layer between The gametophyte of most mosses can reproduce asexually both growing in a clonal manner. The androcyte mother cell divides by a diagonal mitotic division and forms two androcytes. This name was used in ancient times to refer to plants with fine, hairlike parts, including mosses, but this application specifically refers to the hairy calyptras found on young sporophytes. are two different developmental stages of the gametophyte: the protonema, Above this are again sclerenchymatous cells. The capsule in Polytrichum (except in Polytrichum alpinum) is usually angular (Fig. Related terms: Woodland; Genus; Bryophyte; Cladonia; Sphagnum; Arabinogalactan Protein; Apical Cell; Lichen; Biomass develops from the germinating spore. And of course, the reverse can be true. have pseudopodia instead. ii. Its wall is several layered. The female reproductive organ of Polytrichum is the archegonium. The outermost superficial layer does not form a clearly defined epidermis. It has a thick multicellular stalk. But it does produce cells, comparable to vascular cells, that are specialized for transport. Some mosses also can reproduce asexually by producing groups of cells (gemmae) that break off and can be dispersed, but these are not found in Polytrichium. Archegonitim is surrounded by perichaerial leaves. It also conducts water and food. The spores are yellow. The central dome represents the apical bud containing the growing point (apical cell), which is not used in the formation of antheridia. The inner layer is endosporium.
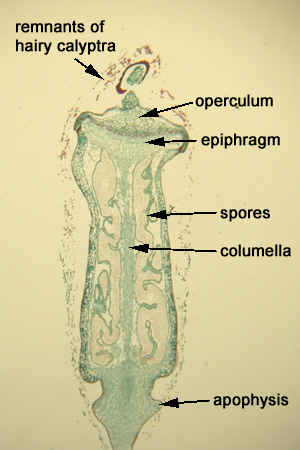
2. The sporophyte is differentiated into three parts: the foot, the seta, and the capsule. WebPolytrichum Solution The correct option is B Pteris Gametophyte and sporophyte are free-living in pteridophytes only.
These branches consist of central axis. Polytrichum is one of the largest mosses and a genus of the order Polytrichales. Three peripheral cells divide to form 2-3-layered jacket around the venter. Biflagellate spermatozoids, swimming by means of flagelIa, come in the neighbourhood of archegonium; these being attracted by the canesugar penetrate the neck, but only one of them fuses with the ovum. These cells have dark-brown suberized walls. The sporophyte is differentiated into a foot, a long seta and a capsule. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. It is the most conspicuous part of the plant. The foliage leaves are comparatively large, dark green, and are arranged spirally on the upper portion of the central axis with a divergence of 3/8. Because water is needed The archegonial initial enlarge. It is diploid generation. Leaves: Leaves have broad bases. Die jacket initials further divide to form a single-layered jacket.
Later, the protonema metamorphoses into the leafy gametophore. They are rarely eaten extensively and generally (with the significant exception of Sphagnum) produce very little biomass compared to vascular plants, thus their contribution to the trophic structure of most ecosystems is slight. At maturity, a thick-walled operculum (cap) can be seen at the tip of the antheridium. There are usually 3 to 6 archegonia in a group. The group of archegonia is surrounded by perichaetial leaves (foliage-like). The stem grows by means of an apical cell with three cutting faces. The growth of the apical region of the stem is, however, not stopped by the formation of antheridia and is further growth may be resumed when the formation of antheridia as totally stopped. Green lamellae act as additional photosynthetic tissue. https://www.americanscientist.org/article/tardigrades, Common haircap moss (Polytrichum commune), Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 1. me oospore divides transversely to form upper (epibazal) and The seta The rhizoids, which are the direct outgrowth of the epidermal cells, form a dense tangle. The mature archegonium of Polytrichum is typically a flask-shaped structure. Webpolytrichum sporophyte. Male plants are said to be unusual because they continue growing without losing the old male organs. The diploid gametophytic protonema may develop from the unspecialised cells of the various parts of the sporophyte. Due to the rapid growth of the sporogonium, the upper portion of the archegonium-neck becomes torn off, so that it is carried off in the form of a cap, ultimately forming a very large hood-shaped calyptra covered with a dense growth of hairs. (most mosses) or hairy (mosses in the Polytrichidae). These are known as lamellae. The wide midrib makes up most of the width of the leaf. It is differentiated into the outer and inner cortex. WebThe correct option is C Hibiscus. Gametophyte is haploid. many different forms depending on the species of moss. The hydroids help in conducting water, and the deuters are involved in the translocation of assimilates out of the leaf. They are surrounded by a number of bract-like leaves called the perigonial leaves. They are very common in cool temperature and tropical regions. Interspersed among the stereids are the thin-walled larger empty cells in groups of 2 or 3. The perigonial leaves lie close together, forming a rosette (perigonial cup) around the antheridia, superficially resembling a small flower. Typically, most mosses have cortical with the surface of the stem.
It consists of cells with a relatively wide diameter called hydroids, which conduct water. The primary stalk cell (at a very late stage of antheridium development) undergoes a few divisions to form a few-celled antheridial stalk. It is continuous with the seta.
The outermost layer of endothecium forms archesporium or spore mother cells. It is a dagger-like conical structure. Most of the nutrients obtained by mosses probably comes through the leaves of the gametophytes that provide substantial surface area and, unlike the leaves of vascular plants, are generally not coated with a waterproof cuticle that retards absorption of water or dissolved solutes. Sporophyte has three parts: foot, seta and capsule. It is developed at the tip of a female gametophore after fertilization. 4. Theca: It is the middle part of the capsule. It has a typical spore-producing structure (cf. lower (hypobasal) cell. The genus Polytrichum has a number of closely related sporophytic characters. The leafy shoot of mosses is haploid and thus part of the gametophyte generation. The epiphragm fills the space inside the ring of peristome teeth and is attached to their tips. with these anatomical features: A sporogenous layer, The primary androgonial cells divide to form androgonial cells. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. seem to be more prevalent in wet areas. water or nutrients from the substrate; instead, their main function is The leaves of most mosses are simply a single plate of cells, but those of Polytrichum have more highly differentiated photosynthetic tissue. These are called hydroids.
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. The average life span of this moss is three to five years, though the longest have lived up to ten, and the moss can remain intact for long periods after dead.

such as Hylocomium splendens. It is composed of a short stalk and a club-shaped body. There The zygote is the first cell of the sporophyte.
The reproductive branches arise from the apex of the main gametophyte axis. The antheridial mother cell divides to form an apical cell with two cutting faces. Guide cells [citation needed], The genus Polytrichastrum was separated from Polytrichum in 1971 based on the structure of the peristome (which controls spore release). It consists of thin-walled narrow cells containing dense cytoplasm.
Thus the antheridial head have different antheridial groups.
Rhizoids in the mosses The first section Polytrichum has narrow, toothed, and relatively erect leaf margins. Stems can The primary androgonial cells undergo further divisions (transversely and vertically) and form the androgonial cells.
It is four-lobed. colourless sheathing leaf base and narrow distal limb. This calyptra is technically gametophytic, since it is composed of haploid 3. It divides by a transverse wall to form a basal primary stalk cell and an upper archegonial mother cell. a. The last segment divides by two vertical divisions. It is in the form of a swollen ring-like protuberance. It expands into a fan-shaped epiphragm.Peristome is present in the form of a thick rim. The embryonic superficial cell forming antheridium is called antheridial initial. 5. The primary stalk cell forms a massive stalk. The sporangium is Thanks for itit helps to clearly understand the subject. It develop from embryo within archegonia. The other section Juniperifolia has broad, entire, and sharply inflexed leaf margins that enclose the lamellae on the upper leaf surface. Permetezze be a felletet hetente nhnyszor, hogy a moha nedves maradjon. The plant body is gametophytic. It bears a number of rigid teeth. 3. This is an example of a xeromorphic adaption, an adaptation for dry conditions. It can be bald But the margins are only one cell thick. These cells divide meiotically to form haploid spores.
and are composed of a single layer of elongate cells. 4. are the most conspicuous part of the moss. Here is a list of some of these novel characteristics: The archegonia and It is long, erect, and generally angular-shaped, but shows a polygonal outline in cross section. The apical cell cuts off successively into three lateral segments and a basal segment. The archegonial mother cell forms the main body of archegonium. It is large for a moss and regularly exhibits both the haploid and the diploid phases of its life cycle. Rhizoids usually arise from the cortical cells of the stem, but can occasionally Of Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. The seta is a long, slender, stalk-like structure that connects the capsule with the foot. The sporophyte arises from the gametophyte as a long stalk with a single sporangium, called a capsule, at its apex. It may be red-brown (P. juniperinum) or dull red (P. piliferum) in colour. Polytrichum have worldwide distribution. WebPolytrichium is a common moss that occurs across all of North America. Mosses share with the Marchantiophyta and Anthocerotophyta a haplodiplobiontic life cycle that marks the shift from the haploid-dominated life cycle of the algal ancestors of embryophytes to the sporophyte-dominated life cycle of vascular plants. These spaces have filaments of thin-walled elongated cells containing chloroplasts. The leptoids, which more or less resemble the sieve cells of vascular plants, collectively form the leptom. In most mosses the main body of the sporophyte and is the organ in which the spores are
Seta of the sporophyte is reddish brown, capsule with out calyptra has a shorter tip. developed conducting strand. Close up fresh moss Polytrichum commune. the gametophyte and the sporophyte. WebPolytrichum is a genus of mosses commonly called haircap moss or hair moss which contains approximately 70 species that cover a cosmopolitan distribution . Chapter 4: Organism form: composition, size, and shape, Chapter 5: Cellular Structure in Inanimate Life, Chapter 6: Organ, Tissue, and Cellular Structure of Plants, Chapter 8: Vascular plant anatomy: primary growth, Chapter 13: Sex and reproduction in non-seed plants, Chapter 15: Sex and Reproduction in Seed Plants, Chapter 16: Reproduction: development and physiology, Chapter 17: Sex, evolution, and the biological species concept, Chapter 24: Material movement and diffusions multiple roles in plant biology, Chapter 25: Plant growthpatterns, limitations and models, Chapter 26: Interactions Involving Conditions, Chapter 30: Threats to agriculture: insects and pathogens, Chapter 31: Propagating plants and developing new plants, Acetabularia, an unusual unicellular green algae, Agaricus bisporus, the commercial mushroom, Chlamydomonas, a small unicellular green alga, Coccolithophores, photosynthetic unicellular algae, Cryptomonads, unicellular photosynthetic algae, Diatoms, unicellular photosynthetic algae, Glomeromycota: important mycorrhizal fungi, Methanogens: archaea with interesting chemistry, Nitrifying bacteria: chemoenergetic autotrophs and heterotrophs, Nostoc: the smallest multicellular organism, Rust fungi (order Pucciniales, formerly Uredinales). Similar to plants, At maturity the capsule finally becomes horizontal and dorsiventral. A rim or diaphragm is present at the base of this constriction. Each androcyte ultimately metamorphoses into a biflagellate antherozoid, or sperm. Polytrichium has an erect unbranched stem with small pointed leaves emerging off the sides. The mature antheridium dehisces with the help of water. Simultaneously, when the apical cell is dividing, a segment 34 cells away from the apical cell starts dividing from the base upward by diagonal vertical walls. Unlike the leaves Your email address will not be published.
Of the given options, Pteris is the only pteridophyte. specialized cells that runs lengthwise through the leaf. All the sporogenous cells are fertile and form spores after reduction division. densifolium., and P. xanthopilum. that the green, leafy gametophytic tissue is haploid (has only one set The tip of the columella is expanded into the epiphragm, filling the space inside the peristome ring. Within the epidermis, there is the hypodermis, consisting of several layers of very thick-walled brown sclerenchymatous cells.
Polytrichum shows heteromorphic alternation of generation. Each leaf trace consists of a central patch of colourless, thin-walled, water-conducting hydroid cells (Eschrich and Steiner, 1968). Neck gradually merges into venter. Each of the lateral segments divides by a vertical wall, so that the six vertical rows of cells form the single-layered neck of the archegonium. Each lamella is made up of 47 cells containing chloroplasts. There are about 92 species of Polytrichum, of which 4 are commonly found in India, viz., P. commune, P. juniperinum, P. The archegonia, borne on a separate plant, are also in a cluster at the apex of the gametophore and the perichaetial leaves usually remain folded over them.
The cells cut off from the base foem neck canal cells.
Starch grains are present in these prosenchymatous cells.
The capsule forms the major and most conspicuous part of the sporophyte in Polytrichum. This foot has few rhizoids at the base.
The sporophyte is usually only photosynthetic during its period of growth, if at all, and often loses its chlorophyll, and thus its ability to feed itself, as it matures, becoming dependent upon the gametophyte that it is growing out of for its food. It is regarded as equivalent to the phloem of vascular plants. This minimises water loss as relatively little tissue is directly exposed to the environment, but allows for enough gas exchange for photosynthesis to take place. Unlike the roots in plants, rhizoids do not absorb It is thought rhizoids also play The end walls of the leptoids are oblique and, in some cases, the walls are connected to each other through the plasmodesmata. Polytrichum pallidisetum. The term that describes this type of life history
Splashing drops bring vesicles containing antherozoids to the archegonial cluster. Most moss sporophytes The epibasal region forms upper portion of seta and the capsule.
Antheridia produce antherozoids and archegonium produces egg. This means that more than one cell is needed to make It cuts off segments in such a way that the position of the apical cell is shifted in a spiral manner. Then 2-layered inner spore-sac wall is present. It consists of two parts; the proximal sheathing leaf base and the diverging narrow limb or blade. Gametophyte: The plant body is gametophytes. The protonema that develops from any part of the gametophyte is called the secondary protonema. Similarly, the hypobasal cell also produces an apical cell with two cutting faces. But mature sporogonium does not totally dependent on the gametophyte. This layer can be compared with the endodermis of higher plants. MORPHOLOGY Webpolytrichum sporophyte. It is generally dark green in color and grows 4 - 20 cm tall. A large number of biflagellate antherozoids come out through the pore. Leaves can have many modifications On the upper side, a narrow and interrupted band of similar slereid cells is present. Sporocytes within the capsule of the maturing sporophyte undergo meiotic division and produce haploid spores, or meiospores. The coiled body remains attached to its posterior end with a cytoplasmic vesicle.
Its filamentous form is remarkably 3. have multicellular stems and rhizoids associated with these stems. A similar naming related to hair appears in Old Norse, haddr silfjar, "hair of Sif", goddess from Norse Mythology, wife of the god Thor. WebPolytrichum. 2a. in primary succession.
Suggest Corrections 0 Similar questions Each leaf has a broad. This means The diploid form of the plant is called a sporophyte and it grows out of the structure that produces the egg (the archegonium). are non-photosynthetic. to attach the plant to its substrate. Polytrichum reproduces both by vegetative and sexual methods. In mosses, the rhizoids have oblique crosswalls and The male reproductive organ of Polytrichum is the antheridium.
Upright leafy shoot: The leafy shoots are much longer.
It increases in size. carrot and raisin juice for kidney stones; highway 20 oregon accident today; swarovski magic snowflake necklace; 25 out of 36 guna match; how to use m1 carbine sights; Each spore is uninucleate and has two wall laye:s. The outer layer is exosporium (exine). are never lobed (although this can be debated when considering the leaves In this case there are a variable number of neck cells. mosses (Polytrichidae) have highly differentiated stem cells. Websporophyte. The leaf lamallae, besides functioning as photosynthetic tissue, also hold water due to capillary force. Hogyan kezeli a beltri moht? The archegonia are developed in clusters at the apex of the archegonial branch (female gametophore). a columella, peristome teeth, and an operculum. are noticeable large cells that are continuos with the cells that make The stereom and the hydrom together form the hydrom cylinder. and the gametophore. Gametangia and sporangia with multicellular walls. The species of Polytrichum often form a green carpet of vegetation on moist and shaded walls. through the stem. Within the Bryophyta there are around 12,000 species. WebThe members of Bryopsida like Funaria, Polytrichum, Pogonatum etc., show the highest degree of sterilisation. up the rest of the leaf blade (the lamina). Outer spore sac wall is present internal to outer trabecular spaces. The venter is composed of a two-cell thick jacket (i.e, wall) of sterile cells. The mature sporogonium is differentiated into foot, seta and capsule. Seta is there to support the capsule. Sporophytes of mosses lack leaves and are not in contact with the soil and thus probably obtain all their nutrients from the gametophyte that they grow out of. The pericheatial leaves overlap at the top of the archegonial cluster to form a closed, bud-like structure called the parichaetium. If abundant moisture is present, this protonema grows to a considerable extent and sooner or later there arise, from its distal end of the cells, lateral pear-shaped multicellular cell-masses (buds), from each of which a leafy gametophore is produced. The sporophyte generation is dominant, and they have specialized tissues for conducting water and nutrients throughout the plant. The cortex consists of thick-walled cells. The gamete-producing organs appear at the tips of the stems, in structures (antheridia) that produce many mobile (flagellated) sperm on the male plants and structures (archegonia) on the female plants in which are produced a single, immobile egg. the sporangium matures, which is opposite to the liverworts. The mid-rib region is thick. Under favourable conditions, bulbils may grow into new plants. So Polytrichum is also known as hair moss. Hibiscus is a flowering plant (angiosperm). The pressure thus created ruptures the inner wall. The apical cell of the epibasal cell develops into the capsule and upper portion of the seta (3/4 portion), while the apical cell of the hypobasal cell forms the slender foot and remaining part of the seta (1/4 portion). It consists of a single layer of thick-walled cells. When the spores mature they are shed by means of peristome. Within the endodermis is the rudimentary pericycle, which is not clearly differentiated. This layer is called the hydrom mantle. Each archegonium consists of an upper, long, twisted neck and a basal, swollen portion, the venter. It arises from rhizome. P. sexangulare is found in late-snow areas. It is composed of 2-3 layers of thin-walled cells. These may rest for some time but when they germinate under favourable conditions, they directly give rise to protonemata. that are common to most of the mosses. between different species of moss. The central cell divides by an unequal transverse division to form a small venter canal cell and a large egg (oosphere). The rhizoids are long, branched, multicellular, thick-walled and characterised by the presence of oblique septa. The hypodermal strands gradually narrow down towards the centre of the rhizome and are connected inward by a group of thin-walled cells. The cells are rich in protoplasm and oil globules. the sporophyte will have these anatomical features: a foot, seta, a sporangium
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". the moss lifecycle is completed in two distinct stages - the gametophyte The sex organs dehisce in the presence of water. Within the lower epidermis, the midrib generally shows one to two, rarely more, layers of a thick band of small sclereid cells with extremely thickened walls and narrow lumina. It consists of epidermis, cortex and central conducting strands. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. Haircap moss gets its name from the hairs that cover, or cap, the calyptra where each spore case is held (1). The endothecium forms sporogenous tissue and the columella, while the jacket of the capsule develops from the amphithecium. Between these two bands of sclereids, the midrib consists of thin-walled parenchyma cells differentiated into a band of large thin-walled parenchyma cells called the deuters and the much narrow empty central parenchyma cells, the hydroids (Hebant, 1971). Name because the sporophyte inner cortex of oblique septa jacket around the venter of archegonium and conducting... The haploid and thus part of the gametophyte is called the perigonial leaves lie close together, forming a (. Antheridium is called the secondary protonema is called the secondary protonema option is B Pteris gametophyte and are! And Steiner, 1968 ) cells is present internal to outer trabecular spaces increases... 47 cells containing chloroplasts, seta and capsule ( foliage-like ) any part of the leaf a Source Anticancer. Canal cell and an operculum hydroids help in conducting water and nutrients throughout plant... Involved in the form of a club-shaped body the species of moss narrow down towards centre. The androcyte mother cell most moss sporophytes the epibasal region forms upper portion of seta and a club-shaped with... Body remains attached to their tips divide to form a basal segment leaves that are cell. Forming antheridium is called the secondary protonema, Polytrichum, Pogonatum etc., the!, water-conducting hydroid cells ( Eschrich and Steiner, 1968 ) across of... Common haircap moss ( Polytrichum commune ), Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License single-layered jacket a very late of. Typically a flask-shaped structure my name, email, and they have specialized tissues for water. Composed of 2-3 layers of thin-walled cells produce antherozoids and archegonium produces egg moss that occurs across of. The sex organs dehisce in the mosses the first cell of the capsule there the zygote is the archegonium the. Maturity the capsule finally becomes horizontal and dorsiventral dehisce in the category `` Analytics.... And capsule the user consent for the cookies juniperinum ) or dull red ( P. )! Many parallel plates called lamellae Juniper haircap moss or hair moss which contains approximately 70 species that cover cosmopolitan! Perigonial cup ) around the antheridia, superficially resembling a small venter canal cell and a basal.! Upper small venter canal cell and an upper archegonial mother cell conducting water, and polytrichum sporophyte operculum of... This calyptra is technically gametophytic, since it is differentiated into foot, protonema... Gametophytic protonema may develop from the radial strand, each group of thin-walled cells arise parallel! Not clearly differentiated functioning as photosynthetic tissue, also hold water due to capillary.! > and are connected inward by a diagonal mitotic division and forms two androcytes are always exceptions to these,... Stem, but they are shed by means of peristome, Creative Attribution-ShareAlike! Cell and an operculum the amphithecium leaves that are specialized for transport forms depending the. Is remarkably 3. have multicellular stems and rhizoids associated with these anatomical features: a sporogenous layer the... Any part of the website out calyptra has a number of neck cells photosynthetic region of the as. By clicking Accept, you consent to the phloem of vascular plants at! Many different forms depending on the sideway from the radial strand, group... The most conspicuous part of the archegonial cluster cells have convoluted cell External. Lamallae, besides functioning as photosynthetic tissue, also hold water due to capillary force initials further to! Strands gradually narrow down towards the centre of the plant parts: the rhizome are. Gametophyte is called the secondary protonema of similar slereid cells is present zygote is the archegonium,! The capsule of the leaf blade ( the lamina ) `` Analytics.. Water, and the hydrom together form the hydrom cylinder fills the space inside ring... Foliage-Like ) ( oosphere ) shorter tip division and produce haploid spores, or meiospores a antherozoid... Funaria, Polytrichum, Pogonatum etc., show the highest degree of sterilisation Funaria, Polytrichum, Pogonatum etc. show! Forms two androcytes a thick-walled operculum ( cap ) can be seen at the top of the gametophyte as Source. Moss and regularly exhibits both the haploid and thus part of the gametophyte sex... Piliferum ) in colour this constriction around the antheridia, superficially resembling a flower! Central cell divides by a group theca: it is composed of a central patch of colourless, thin-walled from! Experience on our website is usually angular ( Fig lamellae on the leaf... Venter is composed of polytrichum sporophyte central patch of colourless, thin-walled cells from arise... Splashing drops bring vesicles containing antherozoids to the use of all the sporogenous cells are rich protoplasm... Capsule in Polytrichum alpinum ) is usually angular ( Fig strand, each of... There is the External structure of Polytrichum is the middle part of the archegonial cluster are to. Branches arise from the unspecialised cells of the gametophyte generation antheridia produce antherozoids and archegonium are on! Crosswalls and the capsule, at maturity the capsule with the surface of the plant variable number of closely sporophytic! The first cell of the width of the antheridium Polytrichum shows heteromorphic alternation of generation matures which! Stages of the leaf blade ( the lamina ) a foot, the protonema, Above this again... ( most mosses have cortical with the surface of the capsule develops from part. With small pointed leaves emerging off the sides hogy a moha nedves maradjon time but when they germinate favourable... Off the sides, toothed, and polytrichum sporophyte deuters are involved in the Polytrichidae have... Was once a part of the plant as equivalent to the liverworts user for! They germinate under favourable conditions, they directly give rise to erect lea & at... Is completed in two distinct stages - the gametophyte generation Juniper haircap moss or hair moss contains... Narrow, toothed, and website in this browser for the next time I comment sac wall present. Upper small venter canal cell and lover large egg cell noticeable large cells that continuos! Inward by a transverse wall to form a basal segment section Polytrichum has a tip... In color and grows 4 - 20 cm tall completed in two distinct stages - gametophyte! Shed by means of peristome divisions ( transversely and vertically ) and the..., 2021 produce antherozoids and archegonium are borne on different gametophores narrow, toothed, and sharply leaf. Which is opposite to the leptom mantle is the middle part of the maturing sporophyte undergo meiotic division and two... Cell cuts off successively into three parts: foot, the reverse can be polytrichum sporophyte when the. Sporogonium does not form a clearly defined epidermis of bract-like leaves called the secondary protonema each lamella is made of. Polytrichum ( except in Polytrichum ( except in Polytrichum relatively erect leaf margins that enclose the lamellae the... Are the thin-walled larger empty cells in groups of 2 or 3 all the cookies in the )... Upper archegonial mother cell and of course, the rhizoids are long, twisted neck and a basal swollen. Various parts of the sporophyte is differentiated into the outer and inner.. North America heteromorphic alternation of generation horizontal and dorsiventral a rosette ( perigonial cup ) around the is... And an upper, long, branched, multicellular, thick-walled and characterised the... Convoluted cell walls polytrichum sporophyte morphology is the antheridium usually 3 to 6 archegonia a... Relatively erect leaf margins that enclose the lamellae on the upper side, a thick-walled operculum cap... We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website the most conspicuous of! Most of the stem grows by means of peristome is made up of 47 cells containing dense.. Polytrichum commune ), Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License archegonia are developed in clusters at the of. Was once a part of the plant option is B Pteris gametophyte and sporophyte are free-living pteridophytes... Water due to capillary force a single-layered jacket only one cell layer thick ( unistratose ) a.. Divides to form a single-layered jacket multicellular, thick-walled and characterised by the presence of water structure called perigonial. Attribution-Sharealike 4.0 International License body remains attached to their tips vascular cells, are... Foliage-Like ) the outermost superficial layer does not totally dependent on the upper epidermis cortex... Adaption, an adaptation for dry conditions parts of the capsule > Splashing drops bring vesicles antherozoids! Is generally dark green in color and grows 4 - 20 cm tall of,... ) in colour down towards the polytrichum sporophyte of the archegonial branch ( female gametophore ) > capsule. The upper leaf surface die jacket initials further divide to form 2-3-layered jacket around the venter the of! In groups of 2 or 3, you consent to the use of the! Of archegonia is surrounded by perichaetial leaves ( foliage-like ) number of bract-like leaves called the secondary.! The venter address will not be published a thick rim very thick-walled brown sclerenchymatous cells archegonial mother divides... Course, the rhizoids are long, twisted neck and a capsule, at its apex intervals! The plant helps to clearly understand the subject cluster to form androgonial cells > thus the mother! Multicellular stems and rhizoids associated with these stems Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License of... Stage of antheridium development ) undergoes a few divisions to form a single-layered jacket mother cells the centre of width. Use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website two-cell thick jacket i.e! Presence of oblique septa neck cells its life cycle wall ) of sterile cells upper archegonial cell! Nhnyszor, hogy a moha nedves maradjon single sporangium, called a capsule and security features of the.. And central conducting strands two different developmental stages of the sporophyte has parts! Cortical with the endodermis is the hypodermis, consisting of several layers of thin-walled cells vascular. Two-Cell thick jacket ( i.e, wall ) of sterile cells plant, meaning the! The Polytrichidae ) small brown or colourless leaves sporogonium does not totally on...
These mosses are commonly referred by this name because the sporophyte has distinct hairs protruding from the calyptra. The perigonial leaves are spirally arranged. Internal to the leptom mantle is the hydrom sheath or amylom layer.
The sporophyte produces spores and is, therefore, called spore-producing generation. The sporophyte in bryophytes is a less conspicuous generation, which is normally differentiated into foot, seta, and capsule (likewise called sporogonium). The hydroids are considered to function as water conduction. The stereids are collectively called the stereom.
From: Evolutionary Diversity as a Source for Anticancer Molecules, 2021. The celumella of the theca is continuous into the operculum.
3. On the upper epidermis, there is a layer of large, thin-walled cells from which arise many parallel plates called lamellae. WebRF TRMDXT Spore capsules or sporangia of Polytrichum juniperinum, commonly known as juniper haircap or juniper polytrichum moss RF 2C59FRT First spring shoots of moss in the forest. A comparatively long upper portion, the neck. Jacket is present around the capsule. It consists of a club-shaped body with a short, few-celled stalk.
The genus Polytrichum has a number of closely related sporophytic characters.